Impact of PCB Material Thickness on Signal Integrity in High-Frequency Applications
Introduction:
PCB material thickness plays a critical role in determining signal integrity, especially in high-frequency applications. Ensuring optimal signal integrity is essential for the performance and reliability of electronic devices. This article explores how varying PCB material thickness can impact signal integrity, providing valuable insights for optimizing PCB designs.
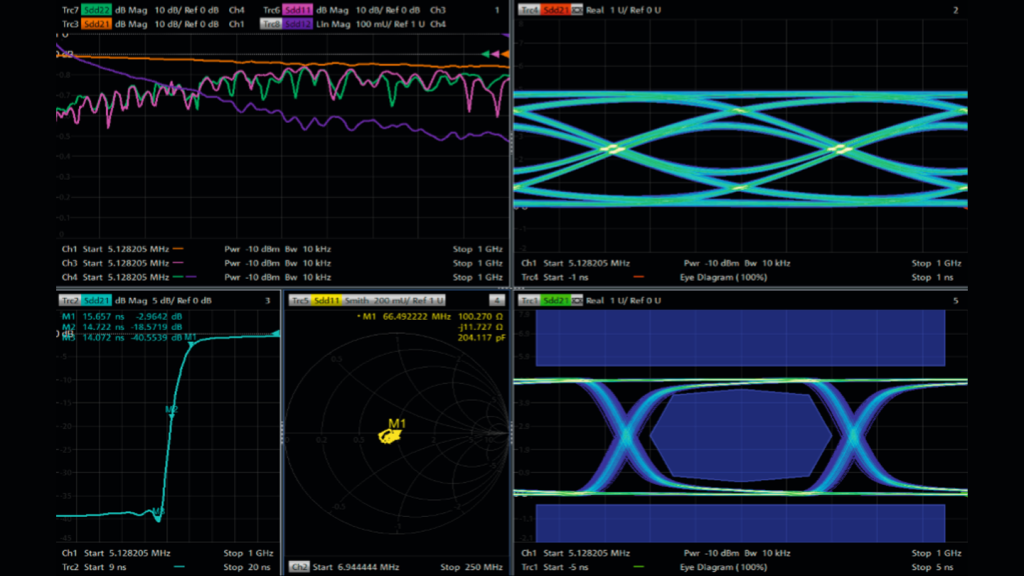
Understanding Signal Integrity in High-Frequency Applications
Signal integrity refers to the quality and reliability of electrical signals transmitted through a PCB. In high-frequency applications, maintaining signal integrity becomes increasingly challenging due to factors like crosstalk, reflection, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). PCB material thickness significantly influences these factors. Thinner PCBs may offer better high-frequency performance due to reduced parasitic inductance and capacitance, while thicker PCBs provide better mechanical strength and thermal management.
Data Table: Effect of PCB Thickness on Signal Integrity
| PCB Thickness (mm) | Signal Integrity Rating |
|---|---|
| 0.2 | High |
| 0.5 | Medium |
| 1.0 | Low |
How PCB Material Thickness Affects Impedance Control
Impedance control is crucial for high-frequency signal transmission, as impedance mismatches can lead to signal reflection and loss. PCB material thickness affects the impedance of the signal traces. Thicker PCBs may require wider traces to maintain the same impedance, while thinner PCBs allow for narrower traces. Proper impedance control helps in minimizing signal reflections and ensuring signal integrity across the PCB.
Balancing Mechanical Strength and Signal Integrity
While thinner PCBs may enhance signal integrity, they can be more fragile and prone to mechanical damage. Thicker PCBs, on the other hand, offer better mechanical strength but may compromise signal integrity in high-frequency applications. It is essential to balance mechanical strength and signal integrity by carefully selecting the appropriate PCB material thickness based on the specific application requirements.

Thermal Management Considerations
Thermal management is another critical factor influenced by PCB material thickness. Thicker PCBs can dissipate heat more effectively, which is beneficial for high-power applications. However, this improved thermal performance must be weighed against potential signal integrity issues. Advanced thermal management techniques, such as the use of thermal vias and heat sinks, can help mitigate the thermal challenges associated with thinner PCBs while maintaining signal integrity.

Minimizing Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can severely impact signal integrity in high-frequency applications. PCB material thickness plays a role in EMI shielding and the overall electromagnetic compatibility of the design. Thinner PCBs may be more susceptible to EMI, while thicker PCBs can provide better shielding. Implementing proper grounding and shielding techniques can help minimize EMI and enhance signal integrity, regardless of the PCB thickness.
Conclusion:
Selecting the appropriate PCB material thickness is vital for ensuring signal integrity in high-frequency applications. By understanding the trade-offs between signal integrity, mechanical strength, thermal management, and EMI shielding, designers can optimize their PCB designs for enhanced performance and reliability. Balancing these factors is crucial for achieving the best results in high-frequency PCB applications.