目录
ToggleEco-Friendly Approaches in PCB Manufacturing: Reducing Environmental Impact
Introduction
In the evolving landscape of electronics, eco-friendly PCB manufacturing has become a crucial aspect of the industry. As environmental concerns rise, manufacturers are increasingly adopting green practices to reduce the environmental impact of printed circuit board (PCB) production. This article delves into various sustainable methods and materials that are revolutionizing PCB manufacturing. From reducing harmful emissions to utilizing recyclable materials, these eco-friendly approaches not only protect the environment but also meet the rising demand for sustainable electronics.

1. Adoption of Lead-Free Solder
One of the most significant changes in eco-friendly PCB manufacturing is the shift from traditional lead-based solder to lead-free alternatives. Lead-free solder, typically composed of tin, silver, and copper, offers several environmental benefits:
- Reduced Toxicity: Lead is a known neurotoxin. By eliminating lead from solder, manufacturers significantly reduce the risk of lead contamination in electronic waste.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regions, including the EU, have strict regulations against the use of lead in electronics (RoHS Directive).
| Solder Type | Composition | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Lead-Based | Tin-Lead (Sn-Pb) | High toxicity, harmful |
| Lead-Free | Tin-Silver-Copper (Sn-Ag-Cu) | Lower toxicity, safer disposal |
2. Utilization of Halogen-Free Materials
Halogenated flame retardants have been widely used in PCBs to prevent fires. However, these chemicals pose serious environmental and health risks. The move towards halogen-free materials in PCB manufacturing offers several advantages:
- Lower Emission of Toxic Gases: Halogen-free materials emit fewer toxic gases when exposed to high temperatures.
- Improved Safety: They reduce the risk of hazardous chemical release during disposal and recycling.
Halogen-free materials maintain fire resistance without compromising the PCB’s structural integrity, making them an eco-friendly choice for modern electronics.
3. Energy-Efficient Manufacturing Processes
Reducing energy consumption during PCB production is another critical factor in minimizing environmental impact. Energy-efficient processes involve:
- Optimization of Manufacturing Equipment: Upgrading to energy-efficient machines can significantly reduce power usage.
- Implementation of Renewable Energy: Using solar, wind, or other renewable energy sources to power manufacturing facilities lowers the carbon footprint.
These energy-saving measures not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also reduce operational costs.

4. Recyclable and Bio-Based PCB Materials
The use of recyclable and bio-based materials in PCB manufacturing is gaining traction. These materials include:
- Recyclable Substrates: Materials like glass-reinforced epoxy are easier to recycle than traditional substrates, reducing electronic waste.
- Bio-Based Polymers: Polymers derived from renewable resources (such as corn starch) can replace petroleum-based materials, promoting a circular economy.
Incorporating these materials helps in reducing dependency on non-renewable resources and facilitates easier end-of-life disposal.
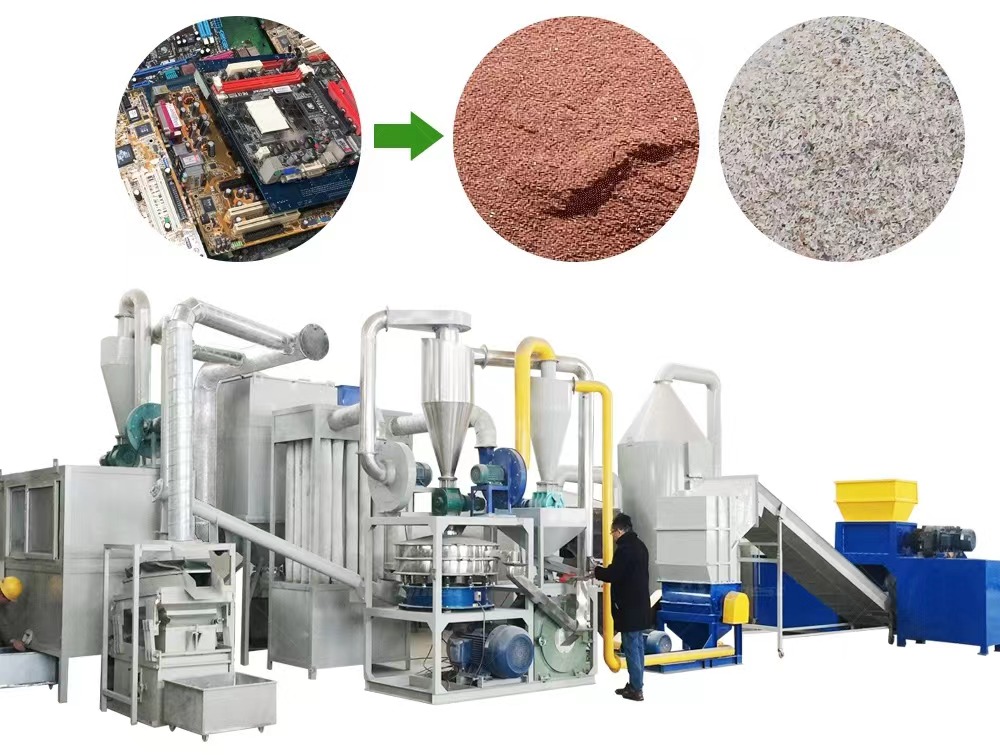
5. Advanced Waste Management Techniques
Efficient waste management in PCB manufacturing is crucial for minimizing environmental harm. Key practices include:
- Recycling of Production Waste: Implementing processes to recycle scrap materials and chemicals used during manufacturing.
- Proper Disposal of Hazardous Waste: Ensuring that harmful by-products are safely disposed of or neutralized to prevent environmental contamination.
These waste management techniques not only align with environmental regulations but also promote sustainable manufacturing practices.

Conclusion
The integration of eco-friendly practices in PCB manufacturing is essential for reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability in the electronics industry. By adopting lead-free solder, halogen-free materials, energy-efficient processes, recyclable and bio-based materials, and advanced waste management techniques, manufacturers can create greener and more efficient PCBs. These approaches not only meet regulatory requirements but also cater to the growing demand for environmentally conscious products.